Internet of Things (IoT)
What is the Internet of Things?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the connection of everyday objects to the Internet so that they can receive, collect and send information.
How does it work? The object collects data from its environment via sensors and sends it over the Internet, Bluetooth, 5G or other networks. This information is processed and analyzed in the cloud and based on this, decisions are made taking into account the data collected.
A leading car maker collects real-time operating data for its 13,000 engines installed in commercial aircraft, allowing it to reduce maintenance times and anticipate failures. The device used by diabetics to measure their blood sugar levels sends the results to their mobile phones and their doctors for close monitoring. Meters and smart grids allow for sustainable and personalised energy management. And thanks to sensors, the devices recognise their environment and collect massive amounts of data.
The world has experimented a lot of changes during the last decade as consequence of technology advances. Artificial Intelligence is already here: it is present in the facial detection function of mobile phones, in virtual voice assistants such as Siri from Apple, Alexa from Amazon or Cortana from Microsoft, in chatbots such as ChatGPT from Open AI and Gemini from Google, and it is integrated into our everyday devices through bots (short for robots) and mobile apps.
Also, there are vehicles that are able to drive by themselfs. Google developed its self-driving car, called Waymo, which is capable of driving for long periods without being connected to the grid and is now operating in the US. Other companies such as Tesla, which has already started testing its driverless taxis, Toyota, Embark, which is looking to apply this technology to trucks, Aurora and Ford, are already looking to move more into this sector.
Applications of Internet of Things
Everything will become smart: cars, homes, cities, industry... Let's look how Internet of Things will affect each one:
Mobility
New technologies will make possible traffic flow analysis, programmable signalling, car park sensors, etc.
In the field of public transport, we will see autonomous buses with autonomous routes, car sharing and, thanks to electric grids, smart energy transport. In agriculture, autonomous tractors will be introduced, enabling more efficient time and work management.
Home
Connected appliances, voice assistants, remote surveillance via mobile or remote HVAC management will be some of the advances that IoT promotes.
With smart meters, every household will also be able to save more on electricity and at the same time pollute less.
Intelligent city or Smart city:
IoT will create more sustainable cities, capable of guaranteeing clean water, supplying realiable electricity, safe gas systems and a efficient public streetlight.
Collection routes will be optimised and all waste comprehensively controlled. In the agricultural sector, innovations such as irrigation programmed according to weather forecasts will reduce water wastage.
In other sectors such as healthcare, we will see innovations such as personal monitoring devices connected to the healthcare system, telemedicine and healthcare resource management through big data. In the world of FMCG, this will be reflected in milestones such as improving the customer’s shopping experience, personalised offers based on customer interactions on social media and advertising and retail intelligence.
Industry
Cyber-physical systems, which combine physical infrastructure with software sensors, communications and process control, etc. will be developed. Experts also warn that 47% of current jobs could be replaced by robots in the future.
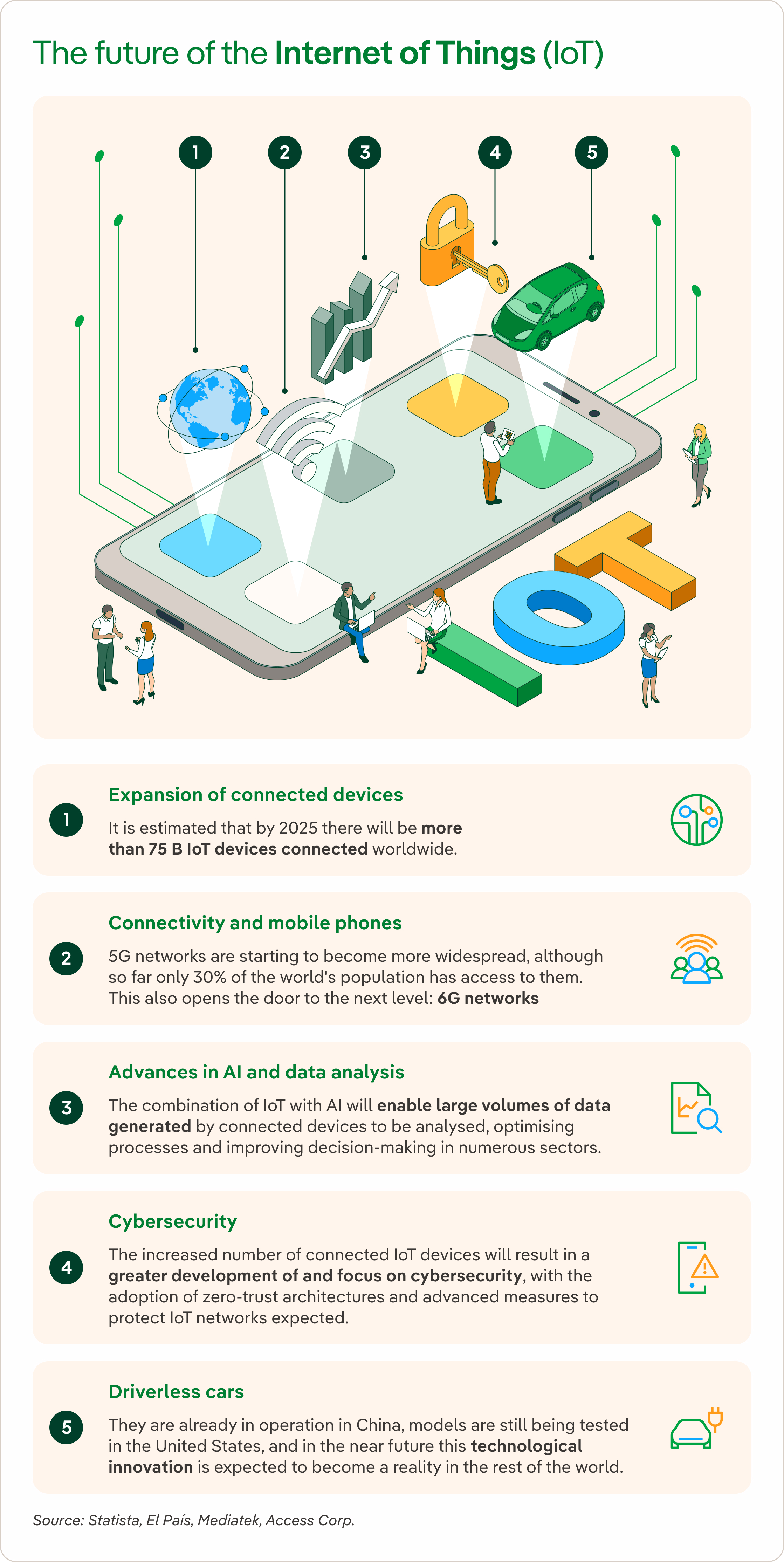
 SEE INFOGRAPHIC: "The future of the Internet of Things (IoT)" [PDF] External link, opens in new window.
SEE INFOGRAPHIC: "The future of the Internet of Things (IoT)" [PDF] External link, opens in new window.
We present you some examples of this applications
Do you know that in 2025 there will be more than 75 B connected devices? Furthermore, in Europe, the smart metering market is expected to reach $13.29 B by 2029. By sector, industry will be the one that will invest the most in the internet of things market, followed by healthcare and transport and logistics.
Within a decade our way of thinking will have changed completely and our future will be hyper-connected, and most of our everyday items will be smart, making our lives easier. Welcome to the Internet of Things!

What are cobots?
The use of cobots in industry is changing production processes.

Hyperautomation meaning
According to the consultancy Gartner, hyperautomation will be one of the technological trends that will have the greatest impact in the next decade.

What is 4D printing and how does it work?
Intelligent designs that adapt to the environment and transform over time.

Digital transformation
Our Strategic Plan 2024-2026 includes an investment of €41 billion to accelerate the energy transition in different sectors.




