World Energy Day 2026
World Energy Day: Commitment and Action for Sustainability
On February 14 we celebrate World Energy Day, a global initiative to raise awareness of the importance of this resource in our daily lives and the need to achieve responsible and efficient production and use of energy resources. In line with our commitment to sustainability, at Iberdrola we work to bring electricity to everyone and optimise its use.
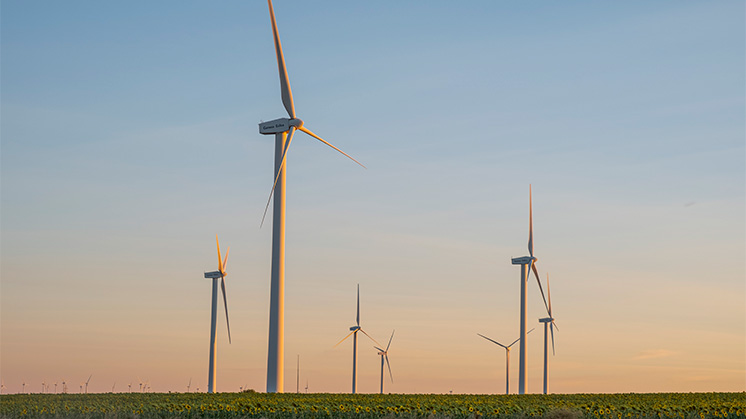

Energy is part of our daily lives: it is the light that illuminates our streets, the air conditioning and heating in our homes and offices, the transport of people and goods or the resources needed to obtain and prepare food, among many other daily activities. But energy is also essential to a country's development, as its economic growth and the quality of life of its inhabitants depend on it. To raise awareness of its importance, World Energy Day is celebrated on 14 February as an opportunity to promote the search for alternatives for a more sustainable future.
According to the scientific community, emissions need to be cut by almost half by 2030 and reach net zero emissions by 2050 to avoid the most negative impacts of climate change. According to the United Nations (UN), fossil fuels (such as coal, oil and gas) are the main drivers of climate change – accounting for over 75 % of total global greenhouse gas emissions and about 90 % of all carbon dioxide emissions.
Fossil fuels continue to account for more than 60% of global supply (down from 82% in 2022), according to the latest report from the International Energy Agency (World Energy Outlook 2024). Renewables, especially solar and wind, continue to grow and are expected consolidate their position as the main source of electricity generation by 2026. However, much remains to be done as can be seen in Electricity Map External link, opens in new window. , a visualisation from an open-source project that depicts how electricity is distributed and generated in much of the world. World Renewable Energy Day calls for action to move this forward.
External link, opens in new window. , a visualisation from an open-source project that depicts how electricity is distributed and generated in much of the world. World Renewable Energy Day calls for action to move this forward.
What is energy?
Energy is an essential property of the universe that manifests itself in different forms and can be defined in various ways depending on the context. Energy is generally understood as the ability of a body or system to perform work or produce a change in itself or others. These changes can be both physical and chemical, for instance, displacement or motion, heat, light or chemical reactions.
Every single change that occurs needs energy in its different forms, i.e. everything around us exists as a result of the action of some source of energy. All living beings grow and develop thanks to it, and machines also need it to function.
Energy follows the universal principle of conservation: it is neither created nor destroyed; it is only transformed into another or transferred to another body, and can exist in various forms, such as kinetic energy, potential energy, thermal energy, chemical energy, and so on. However, Energy Day highlights the particular relevance of electricity in our daily lives.
Electrical energy is the movement of electrons (negative charges) between two points when there is an electrical potential difference between them, which are brought into contact through a transmitter or conductor, such as a metal wire. As a result, an electric current is generated used to power a wide variety of electrical devices and systems. It is the form of energy that can be most easily transformed into other forms.
The origin of World Energy Day and its importance
The UN established World Energy Day on 14 February 1949 to invite reflection on energy efficiency and production alternatives. The First International Conference held in Austria in 1998 –where more than 350 experts and leaders from 50 countries met to discuss strategies to address the energy crisis and possible solutions– reinforced the importance of this date and of moving forward an efficient development. This meeting gave rise to new related events such as the World Energy Efficiency Day.


Clean energy
Clean energies are positioned as an alternative to preserve the environment.

Electrify the economy
We support decarbonisation through increased electrification.
Types of renewable energies
Renewable energies, essential for a sustainable future, are those generated using natural sources that will never run out, and are continuously renewable. They are environmentally friendly resources and help reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Some of the main types of renewable energies are:
![]() Wind energy
Wind energy
This is the energy generated using wind, i.e. by harnessing the kinetic energy of air masses using wind turbines. Depending on where these wind turbines are located, we can speak of onshore wind energy or offshore wind energy. It has been used for centuries, with the technologies available at any given time and with different functions.
![]() Solar energy
Solar energy
This type of energy is obtained by harnessing electromagnetic radiation from the sun using collectors such as photovoltaic cells. Photovoltaic solar energy is based on the so-called photoelectric effect, by which certain materials are able to absorb photons (light particles) and release electrons, generating an electric current.
![]() Hydraulic energy
Hydraulic energy
This is generated by transforming the potential energy existing between two bodies of water located at different altitudes or elevations into electrical energy. In order to obtain hydropower, also known as hydroelectric power, infrastructures capable of extracting the maximum potential from this resource are built.
![]() Geothermal energy
Geothermal energy
This energy comes from the internal heat of the earth. Geothermal energy can be used directly for heating or to generate electricity through geothermal power plants.
![]() Ocean energy
Ocean energy
Includes various forms of harnessing, such as wave energy (waves), tidal energy (tides) and ocean thermal energy (temperature difference between water layers).
![]() Biomass energy
Biomass energy
It comes from organic materials, such as agricultural or forestry residues. It can be used to generate electricity, heat or biofuels.
Iberdrola's commitment to a sustainable energy future
Commitment to a decarbonised society is everyone's task. For this reason, at Iberdrola we are working to achieve a sustainable future and we are committed to leading the electrification, a challenge that we undertook more than two decades ago, when we decided to commit to renewable energies to build our clean, reliable, and clean business model. To achieve this goal, we are promoting three main actions.
- Renewable energy deployment. If the goal is to achieve the decarbonisation of society, it is essential to achieve maximum integration and stability of renewable energies. We are currently a world leader in this area.
- Boosting technological innovation. Technological evolution enables the evolution of the entire sector: from improvements in power generation to the drive for smart grids and the provision of new services to customers, among others.
- Electrification of the economy. Electrification of the economy, transport and buildings is the main energy vector of the energy transition towards decarbonisation that can best incorporate renewable energies.
Aware of our role as a driving force, Iberdrola continues to invest in these areas and we are leading climate action with different events, multilateral agreements and alliances to fight against climate change.




