Wind turbines blades
Eight interesting facts about wind turbine blades
Have you ever wondered how a wind turbine tower can support so much weight? Or why they are all orientated in the same direction? This is the nature of wind turbines, the giants of renewable energy.

When travelling by road a little way away from cities you must have come across a wind energy farm. It is curious to see how wind turbines appear to work in sync. It's like watching a football team, with all of the members placed strategically and turning in the same direction.
It may seem like a coincidence, but it is not: All of the details of the operation are governed by well-studied and well-defined research. Find out more about them!
Why are the most commonly used wind turbines those with three blades?
Throughout history, there have been many types of turbines or machines that were used to take advantage of the kinetic energy produced by the wind. Of all of these, the most used and widespread in our days — and likewise chosen by Iberdrola — is one which has three blades moving with respect to a horizontal axis. This is the most efficient option from the technical point of view: having fewer blades leads to better balance.
Why do they always face in the same direction?
Like a field of sunflowers, wind turbines are always oriented in the same direction so that, instead of following the sun, they may follow the wind and harness its potential energy. This is achieved thanks to a weather vane that they all have on top of the nacelle. This weather vane indicates to the control whether the rotor is correctly positioned against the wind.
How does the wind manage to move the blades?
Sometimes it is hard to imagine how the blades of a wind turbine, laden with such size and weight, are able to be moved by a wind with normal characteristics. The reason is due to its shape, the so-called aerodynamic profile: When the wind blows perpendicular to them, a lift force is generated that causes the movement.
How does the tower hold up so much weight?
A wind turbine tower is the structural component onto which the rotor and the nacelle are fixed. Moreover, it supports the entire force of the wind. The key is in its design and composition, as it must be able to bear the weight of up to 15 adult elephants.
Do you know how the blades of a wind turbine are made?
Find out about the manufacturing phases of the blades
-
Manufacturing of the beam: this is the inner part of the blade and is composed of materials formed of fibreglass and carbon pre-coated with epoxy resin - a thermostable polymer that hardens when mixed with a catalyst agent.
-
Manufacturing of the shells: they cover the girders and are made of fibreglass. In addition, they are covered by a layer of paint, which provides protection.
-
Assembly and curing: after obtaining the two shells, the next step is to bond the girder between the two shells and have them pass through an oven to form a single firm and strong structure.
-
Finishing: once the leading and trailing edges of the blade are finished, the structure undergoes a new inspection prior to the blade being moved to its destination wind farm.
-
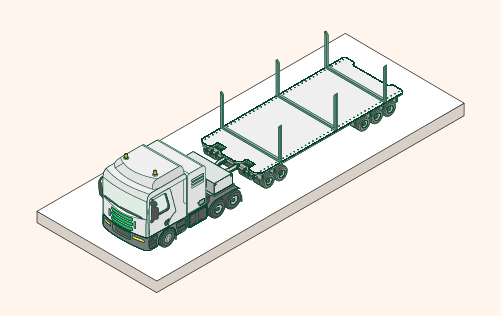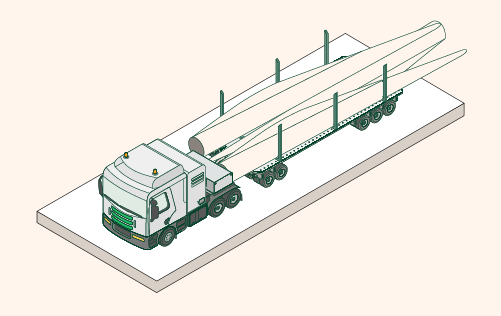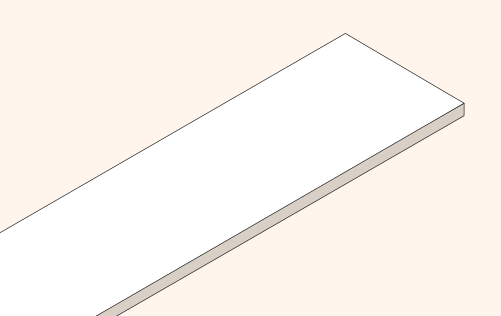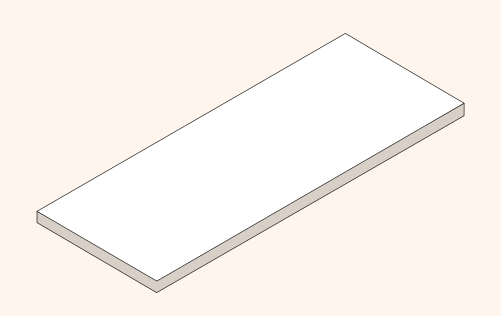
Transportation and installation: the blades of a wind turbine are very heavy, massive structures. The blades of the Saint Brieuc offshore wind farm, for example, have a length of 82 meters. The require specialised forms of transport that are capable of loading these structures and carrying them to their destination. At the destination, an experienced team of people assembles the blades and the rotor on the nacelle.

History of offshore wind energy
Discovering the evolution and impact of offshore wind energy.

Recycling of wind turbine blades
Most wind turbine components are recyclable.

All about wind turbines
Discover what wind turbines, the giants of renewable energy, look like.

Installation of wind turbines
What is the most efficient place to install a wind turbine?
How much energy do wind turbines create?
Understanding how much energy do wind turbines create is essential for evaluating their efficiency and impact. On average, small wind turbines can generate between 5kW to 100kW, sufficient for individual households or small businesses.
Medium-sized turbines typically produce between 100kW and 1MW, catering to community or industrial needs. Meanwhile, large-scale wind turbines, especially those used offshore, can generate between 2 MW and 12 MW or more, making them capable of powering thousands of homes.
Thereover, the amount of energy produced by wind turbines varies widely depending on their size and location, highlighting their versatility in renewable energy production.
How long do wind turbines last: key factors
Usually, a modern turbine is designed to operate for about 20 years, depending on environmental factors and the correct maintenance two to three times per year, this lifetime can extend up to 25 years or even more.
While turbines are built to endure substantial stress, their longevity is determined by the amount of load and stress the structure is put under by the wind, especially since the structure is only fixed at one end.
The main factor that determines the life of the wind turbine is the environmental condition, both natural wear and the need for careful management and maintenance.
Parts of the windmill: their components and roles
The parts of the windmill work together to harness wind energy effectively. Key components include the rotor blades, which are designed to capture the wind and convert it into rotational energy. This rotation is transmitted through the hub to the main shaft, which then drives the gearbox.
The gearbox adjusts the speed of rotation to suit the generator, located in the nacelle, which produces electricity. The tower provides the necessary height to access stronger winds and support the entire assembly.
Each part of the windmill plays a crucial role in the generation of wind power.
The size of blades on a wind turbine
The size of blades on a wind turbine is mandatory for its efficiency. To produce electricity, blades on a wind turbine varies in sizes. The smaller turbines have blades from 120 to 215 feet: these ones are ideal for residential or minor scale energy needs.
The medium sized turbines have blades between 215 and 275 feet and are commonly used for community power generation. For large sized turbines, the size of blades on a wind turbine is 280 feet, enabling the generation of several megawatts of power.
The size of blades on a wind turbine is adapted to match the scale and location of its energy production requirements. The different sizes have in common the materials, aerodynamic design to capture the maximum amount of wind and its focus on energy conversion efficiency.