Wind Energy
What is wind power, how is it converted into electricity and what are its advantages?
Wind energy, which transforms the power of an inexhaustible resource such as wind into electricity, is a sustainable and valuable investment for the future. Utilising wind requires the construction of wind farms, either on land or at high sea, with dozens of wind turbines. These giants have become part of the landscape in recent years, but do we know how they work?

How is wind generated? Solar radiation does not affect the earth's surface equally: some areas are warmer than others, and in these areas the air, which weighs less, tends to rise, creating low pressure areas, while in colder areas the air descends and weighs more, creating high pressure areas. The difference in pressure causes the air to move and creates wind, an element so powerful that it can be used to generate energy.
What is wind energy
Wind power is energy obtained from the force of the wind. How? Through a wind turbine that transforms the kinetic energy of air currents into electrical energy. The energy is mainly extracted with the rotor, which transforms the kinetic energy into mechanical energy, and with the generator, which transforms this mechanical energy into electrical energy. We are talking about a renewable, efficient, mature and secure energy that is key to the energy transition and the decarbonisation of the economy.
How does wind power work. Characteristics
Wind Turbines
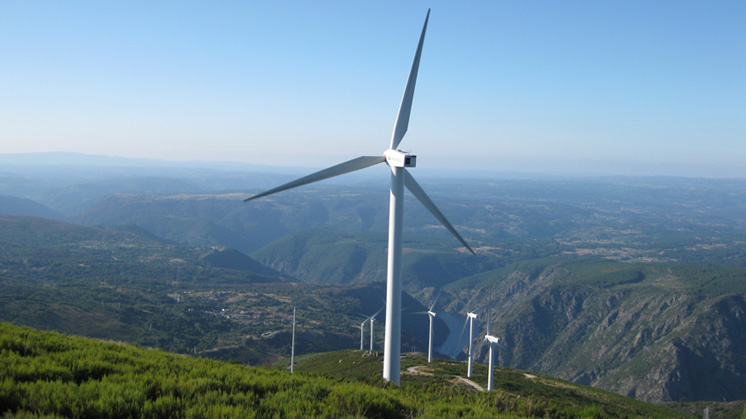
As we have already mentioned, in order to utilise the kinetic energy of the wind and convert it into electrical energy, it is necessary to use a wind turbine. The optimal use of these giants, (they are usually between 80 and 120 metres high) depends on the strength of the wind. For this reason, wind farms, which pool a large number of wind turbines and make it possible to obtain this energy in large quantities, must be set up in places where windy conditions are predominant.
The wind turbines have to be oriented in the direction of the wind, which is done by means of a vane on the nacelle. From there, the force of the air currents will set the three main parts of the wind turbine in motion:
-
The rotor: composed of three blades and the bushing that joins them together, its function is to capture the force of the wind and convert it into mechanical rotational energy.
-
The multiplier: connected to the engine by means of a shaft, its function is to increase the rotational speed from 30 revolutions per minute (rpm) to 1500 rpm.
-
The generator: this element is responsible for converting the mechanical energy of rotation into electrical energy.
Each of the wind turbines that make up a wind farm are linked together by underground cables that carry the electricity to a transformer substation. From there it is transported to homes, factories or schools, among other recipients, through the distribution networks of the various electricity companies.
Wind energy, clean, efficent ans safe
Wind power installations
- Onshore wind
- Offshore wind
In Europe
- 2023 238 34
- 2022 224 30
- 2021 209 28
- 2020 195 25
- 2019 183 22
- 2018 171 18
- 2017 162 16
- 2016 149 12
- 2015 137 11
- 2014 126 8

272 GW installed wind power capacity in Europe
Source: Wind Europe, Wind energy in Europe in 2023
Around the world
- 2023 946 75
- 2022 842 64
- 2021 774 56
- 2020 709 36
- 2019 621 29
- 2018 568 23
- 2017 522 19
- 2016 473 14
- 2015 421 12
- 2014 362 8
- 2013 312 7

906 GW installed wind power capacity in the world
Source: Global Wind Energy Council, Global Wind Report 2023
Parts of a wind turbine

A wind turbine is a sophisticated piece of engineering. Its size means that it is built in parts and assembled on arrival at the wind farm.
We will analyse the characteristics of each of its parts.
- Blade
- Hub
- Rotor diameter
- Tower
- Anchor ring
- Foundations
- Piles


- Blade
- Low-speed shaft
- High-speed shaft
- Power cable
- Yaw mechanism
- Multiplier
- Electric generator
- Electronic control
- Nacelle
- Tower
- Cooling unit
- Brake
- Wind vane and anemometer
- Rotor
 SEE INFOGRAPHIC: Wind energy: clean, efficient and safe [PDF] External link, opens in new window.
SEE INFOGRAPHIC: Wind energy: clean, efficient and safe [PDF] External link, opens in new window.
Types of wind energy
There are currently two types of wind energy depending on where the wind turbines are erected:
Onshore wind energy
Onshore wind energy is responsible for producing electricity by harnessing the wind from wind farms located on land. To do this, we install wind turbines capable of transforming kinetic energy from the wind into electricity suitable for use and send it to the distribution network.
Offshore wind energy
Offshore wind energy is the energy obtained by harnessing the force of the wind that is produced on the high seas, where it reaches a higher and more constant speed than on land due to the absence of barriers. In order to make the most of this resource, mega-structures are installed that are seated on the seabed and equipped with the latest technical innovations.
Advantages of wind energy
Wind power offers numerous benefits, both for the companies that invest in it and for society by helping to minimise the impact of climate change:
 Clean
Clean
As it does not require any combustion process, it is an energy with low greenhouse gas (GEI) emissions, the main culprits of global warming.
 Inexhaustible
Inexhaustible
Wind is an unlimited resource, and so is its use as long as there are sufficient air currents.
 Cheap
Cheap
Both the cost per kW produced and its maintenance is quite low. In areas where the wind blows harder, the benefit is even greater.
 Low impact
Low impact
Wind farms are built after a rigorous analysis and planning process. In addition, depopulated areas are sought to avoid negative effects on inhabitants.
 It generates green jobs
It generates green jobs
According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), wind energy already employs more than 1.2 million people today and the number of green jobs will not stop growing.
How a wind farm is built
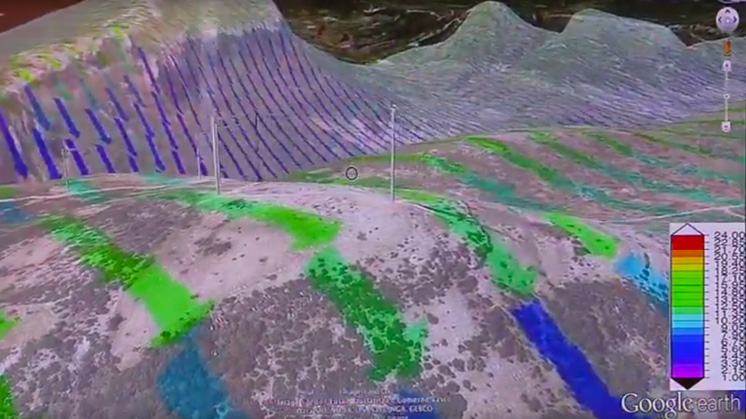
The process involved in building a wind farm is very complex since there are many characteristics that must be analysed to know where and when it should be built. Of these, the most important characteristics that must be analysed are the spatial, temporal and vertical variation of wind through time. These parameters are studied with wind vanes and anemometers and the future production of the wind farm is estimated to guarantee its potential efficiency. Cutting edge supercomputing techniques optimise the design of the wind farm complex to maximise the generation of energy.
Innovation is also allowing us to make great progress in offshore wind energy. An example is the Romeo project, a European initiative led by Iberdrola to reduce the operating and maintenance costs of wind farms.
Iberdrola, pioneer in onshore wind power for 20 years, now stands out in offshore wind power with new projects and markets.

What is onshore wind energy
Find out how onshore wind farms work.

Installation of wind turbines
What is the most efficient place to install a wind turbine?

Wind measurement
We tell you how it is done, why it is so important and the latest news.