Design Thinking
Design Thinking: a different way of thinking and acting
Although the methodology is not new, Design Thinking is increasingly present in the business world because of its ability to generate innovation in the development of new products and services. The key? It is a different way of thinking and acting that not only gives rise to innovative ideas, but also drives and strengthens talent.

Design Thinking is a working method that faces and solves the challenges and problems that arise in companies based on creativity, multidisciplinarity and teamwork. This different, experimental and holistic approach can give rise to what all companies pursue: innovation. Its many applications are limited by our own imagination and it allows products to be created that change the game rules.
According to experts, its origin dates back to 1919, when the German architect Walter Gropius created the Bauhaus school of crafts, design, art and architecture. The school began to establish many of the dynamics that are used today in Design Thinking, such as teamwork, the elimination of hierarchies in the innovation process and the project approach to user needs.
The technique was developed at theoretical level in the 70s, at Stanford University (California), and two decades later, in 1991, the North American design consultancy, IDEO, gave it a final drive by setting up, for the first time, multidisciplinary teams — professors, lawyers, engineers and doctors — to work on different projects, thus laying the foundations of modern Design Thinking.
What is Design Thinking and what is it for
When we talk about Design Thinking we are talking about a methodology that, when taken to the business environment, advocates facing the difficulties — and also the opportunities — just as designers face the design process. And how do they do it? First, they define user needs by focusing on the person and not the product, using observation and empathy. Second, they establish a multidisciplinary working approach during all phases to generate innovative and disruptive solutions.
Ideas arising from a methodology such as Design Thinking bring value to the customer and provide a market opportunity for the company, but can also be applied to create better work processes or define new business models. From a more practical point of view, the dynamics even help to generate a good atmosphere in the company, reinforce teamwork and, of course, boost creativity. "If you can't draw it, you don't understand it," Einstein said. This methodology solves this problem by developing very creative techniques mixing the analytical and the visual.
Phases of Design Thinking
The process consists of five clearly defined stages:
 Empathise
Empathise
The quintessential source of information is people and what they experience in relation to a product. Therefore, unlike traditional techniques, which use statistics, here the needs, problems and desires of the user need to be deeply understood.
 Define
Define
With the information obtained in the previous stage, a filter is made and a selection of whatever provides value and can lead to new perspectives and innovative results. They also begin to identify potential problems.
 Devise
Devise
The different approaches of the multidisciplinary teams are fundamental in finding the idea that will be put into practice. The key is to encourage participation and not to discard anything a priori, because sometimes the most bizarre ideas can end up being disruptive.
 Prototype
Prototype
The time has come to make ideas a reality. Building physical or digital prototypes through 3D printers or software turn the idea into something tangible that makes it possible to detect problems and find solutions without incurring large costs.
 Test
Test
In this last phase, the user involved in the whole process interacts with the prototype, and their feedback helps us identify faults and shortcomings and make the necessary improvements or amendments to the final product or service.
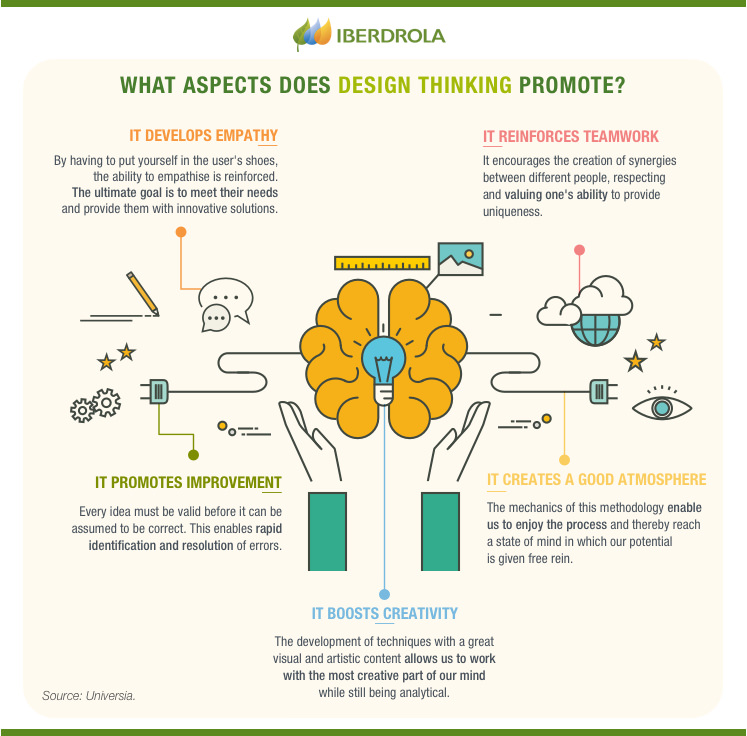
SEE INFOGRAPHIC: What aspects does Design Thinking promote? [PDF] External link, opens in new window.
Main Design Thinking techniques
There are countless techniques to address Design Thinking. We present the most common ones below:
 Mind map
Mind map
A visual tool that helps to develop a certain idea, thought or concept. According to Tony Bouza, its creator, "It favours fluidity, improves understanding and helps to fix and understand complex ideas." Just place the keyword or idea in the centre of the map and connect it with other related words.
 Customer Journey
Customer Journey
Defines the different activities that a user carries out when using a product or service. These activities can be guided by the client's needs at any given moment and the touchpoints between them and the company behind the product or service.
 Glocal
Glocal
Is the acronym for global and local. This consists on researching and studying both local and global current trends related to the challenge posed, in order to apply or not apply them to the project.
What are you waiting to start using Design Thinking and boost your talent?
Mindfulness, the technique of the here and now
The advantages of collective intelligence




