International Day of Clean Energy: 26 January
International Day of Clean Energy: discover its history
The International Day of Clean Energy is celebrated on 26 January, a global event that aims to raise awareness and mobilise for a fair and inclusive progress transition to clean energy for the benefit of people and the planet. In line with our commitment to sustainability and climate action, at Iberdrola we work to promote a sustainable and efficient energy model for all.
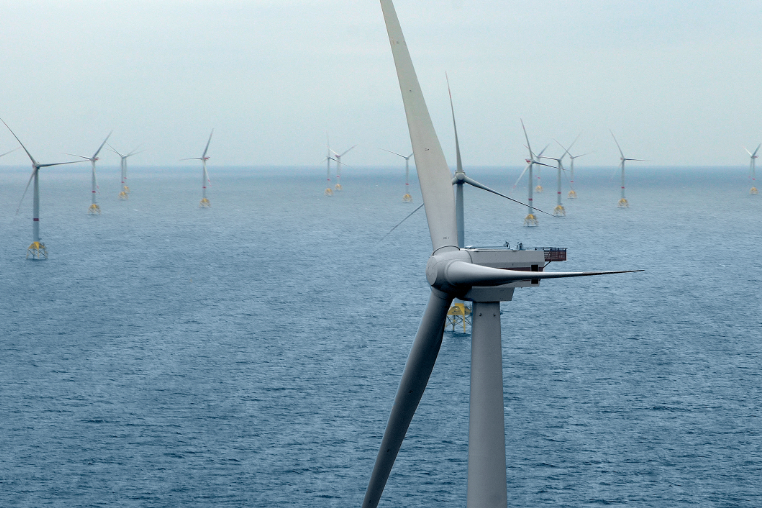
Wikinger offshore wind farm.
The climate crisis is one of the greatest threats facing human beings in the 21st century, in which the electrification is emerging as the way forward to achieve a clean, sustainable and secure energy model. It is our duty as a society to find solutions and build a legal framework that addresses the climate problem and paves the way for energy transformation. The international community points to the deployment of clean energy as a key factor in ensuring a more sustainable future.
What day is the International Day of Clean Energy?
International Day of Clean Energy, which is celebrated every 26 January, aims to raise awareness, call to action and mobilise society in the development, deployment and use of clean energy to ensure a fair and inclusive progress sustainable model for all.
The UN General Assembly chose this day to commemorate the anniversary of the founding of the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) in 2009. Its connection is clear: this global intergovernmental agency was created to support countries in their progress towards the energy transition as well as to become a platform for international cooperation around and a benchmark in statistical analysis of clean energy technologies, innovation or investment.
How to celebrate the Day of Clean Energy?
The International Day of Clean Energy is an opportunity to rethink the future of the planet and to take action to ensure a more sustainable future. During the day, events are held at the international, national and even regional levels. Institutions and organisations plan conferences, panels and workshops on the importance of clean energy, awareness-raising campaigns are launched on the importance of clean energy and exhibitions on clean energy technologies are organised. Sometimes concerts and cultural events are held and new initiatives are announced.
Anyone can celebrate this day by claiming the importance of clean technologies by participating in these events, spreading their use over social media and committing to include new sustainable practices that promote their use. It is an excellent opportunity to reflect on the everyday actions we can take to reduce our carbon footprint. From using public transport or bicycles to adopting more efficient technologies at home, every little gesture counts.
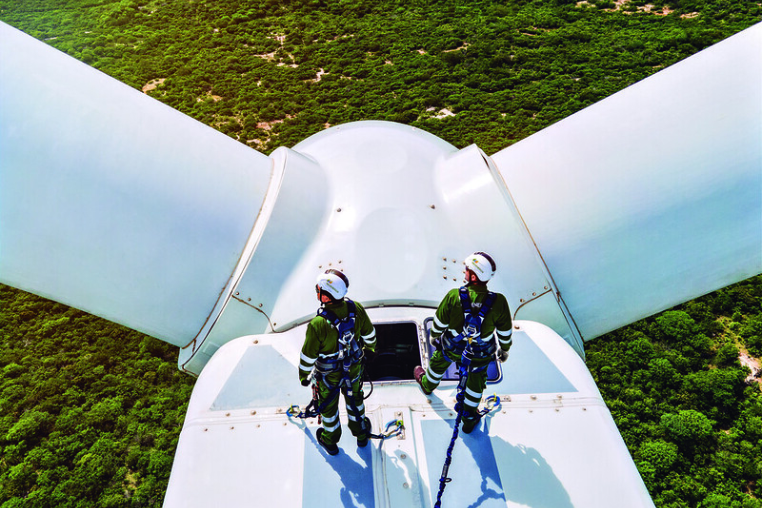

At Iberdrola we are committed to a clean, reliable and smart business model that prioritises clean energy.

At Iberdrola we are committed to a clean, reliable and smart business model that prioritises clean energy.

At Iberdrola we are committed to a clean, reliable and smart business model that prioritises clean energy.

At Iberdrola we are committed to a clean, reliable and smart business model that prioritises clean energy.
History of clean energy: discover its evolution
The first forms of clean energy date back to ancient times in the form of windmills and watermills in Persian, Egyptian and Roman civilisations. These applications harnessed natural resources for mechanical tasks such as washing, tanning, grinding grain or pressing raw materials. Energy production for distribution came centuries later and during the Industrial Revolution in the 18th century, fossil fuels –especially coal– almost completely displaced these primitive forms of clean energy due to their widespread availability.
The turning point came in the 1970s in the form of the energy crisis that shot up oil prices. Many countries felt the need to look for alternative forms of energy to help them reduce their dependence on fossil fuels. The first developments in clean and renewable energies emerged at this time, especially modern wind and solar technologies.

"We’re certainly going very slowly. We’ve already almost reached the temperature levels we expected by 2050. We have time if we triple renewables by 2030 and reduce fossil fuel consumption"
Ignacio S. Galán
Executive Chairman of Iberdrola
The 21st century arrived with growing concern about climate change, which led to the global rise of clean energies as a means of promoting a more sustainable model. Technological evolution and international policies to reduce emissions, with the Kyoto Protocol (1997) and the Paris Agreement (2015) as their main exponents, focused on this type of technology and promoted significant advances in their efficiency, innovation and profitability. Clean energy is now a real, viable and scalable alternative to transform the way we produce and distribute energy.

Clean energy
Clean energy comes from generation systems that do not produce any kind of pollution-

Carbon footprint
What is the carbon footprint and why will reducing it help to combat climate change?

SDG 7
Affordable and clean energy, what is it and why is it so important?

Innovation in renewables
We innovate to improve the efficiency of our renewable assets and accelerate their integration into the electricity system.
What are clean energies? Exploring clean energy sources
Clean energies are energy production systems that do not pollute, especially through releasing greenhouse gases such as CO2, which cause climate change. This type of technology does not have a negative impact on the environment during production or consumption. Clean energies –well underway– boost efforts to protect the environment and alleviate the crisis of exhaustible energies, such as gas and oil.
Clean energy and renewable energy are two concepts that are often associated but do not have the same meaning. The main difference lies in their environmental impact. Renewable energies, surprising as this may be, can pollute. Their definition refers to the fact that they regenerate naturally in a shorter period of time than fossil fuels. Although they are sustainable in the long term and almost always clean, it is true that they can have some environmental impacts during their use.
Biogas or biodiesel, for example, are renewable energy sources because, among other things, they come from inexhaustible natural sources. However, unlike most renewable energies, they pollute through their combustion by emitting greenhouse gases.
On the other hand, clean energies have a minimal environmental impact and do not pollute. So we can say that most renewable energy sources are also clean and vice versa. These are some of the most common clean energies:
What is clean energy for?
The international scientific community agrees that emissions need to be cut by almost half by 2030 and reach net zero emissions by 2050 to avoid the most negative impacts of climate change. Fossil fuels, the main drivers of climate change, are responsible for more than 75% of global greenhouse gas emissions and approximately 90% of all carbon dioxide emissions on the planet, according to the United Nations (UN).
In addition, the World Health Organisation (WHO) estimates that air pollution causes around 7 million deaths a year, many of which are closely linked to the burning of fossil fuels.
Replacing coal and oil with clean sources can significantly reduce the emission of harmful particles and improve people’s health. The Day of Clean Energy calls for the advancement to a healthier, greener and more resilient model.
Clean energy characteristics
Clean energies have some key characteristics that make them key to a sustainable energy future:
Clean energy use: the energy of the future
The use of clean energy sources is crucial to cope with future increases in global energy demand as well as to mitigate climate change. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global energy consumption could increase by 25% by 2040 due to population growth and economic expansion, especially in developing countries. Without a shift to clean sources, this rise could turn into more greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuel use.
In addition, the Paris Agreement sets a goal of limiting global warming to 1.5°C to avoid irreversible damage to the environment. If this does not occur, the world would face increasingly frequent and costly extreme weather events. Carbon emissions must be reduced to net zero by 2050, requiring clean energy to account for almost 90% of global electricity generation by then. Adopting clean energy on a large scale will make it possible to meet growing demand in a sustainable way and reduce the negative effects of polluting energies.
Iberdrola's leadership in clean energies
At Iberdrola Group, we are world leaders in renewable energy sources and we lead the electrification towards a low-emission economy. These types of technologies are the essential pillars on which we build our clean, reliable, and smart business model.
This commitment is reflected in practice in our Strategic Plan 2025-2028. Iberdrola continues to advance its pledge to accelerate the electrification of the planet and aims to reconcile its growth with active efforts to achieve emissions neutrality in electricity generation by 2030.