-
Shopping for loose produce has become popular again to reduce food wastage and help to halt the avalanche of plastic packaging which is damaging our planet. This way of shopping, which was commonplace until only a few decades ago, enables us to buy foodstuffs and other household products by weight and without packaging, and has become a mainstay of the global zero-waste movement.
New York City (USA) became the epicentre of the climate agenda in September 2019. The city hosted two pivotal events to measure the degree of commitment to global warming. These are the United Nations Climate Action Summit on 23 September and the Climate Week NYC from 23 to 29 September. The next United Nations Conference on climate change (COP25) was held in Chile.
-
The fight against climate change needs more than just good intentions. Adaptation and mitigation processes, crucial to stopping the planet from deteriorating over the coming decades, requires financing, and this flow of money can come from both private and public sources. The United Nations, though the UNFCCC, is responsible for supervising transfers from developed to developing countries.
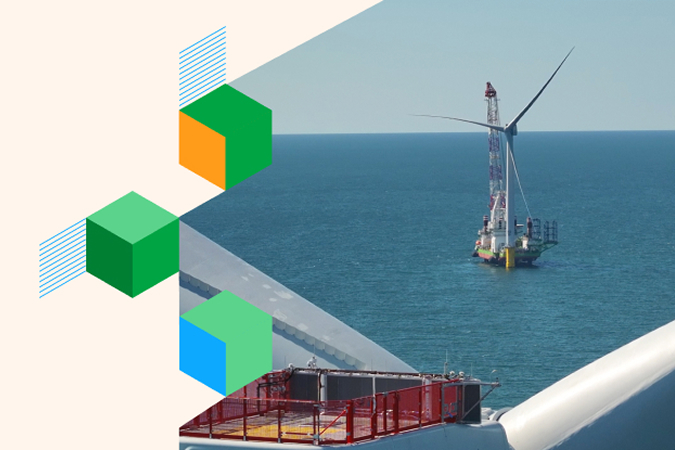
The Katowice Climate Summit (COP24) will take place from 2nd to 14th December under Poland's presidency and will constitute a real milestone in the global climate action agenda. We analyse, in detail, its progress and possible results.
-
Facebook COP24 will establish the instruments to be used to comply with the Paris Agreement and will send strong signals to governments and civil society
-
Twitter COP24 will establish the instruments to be used to comply with the Paris Agreement and will send strong signals to governments and civil society
-
Linkedin COP24 will establish the instruments to be used to comply with the Paris Agreement and will send strong signals to governments and civil society
-
Whatsapp
-
-
Plastic is environmentally harmful because it does not degrade: did you know that plastic bottles can take more than five centuries to break down? But, what if bottles and other plastic waste could be transformed to our advantage? Armed with this challenge, researchers from Rutgers University in the United States have created a 100% recycled and recyclable thermoplastic material which is now being used in construction. This led to the creation of the world's longest recycled plastic bridge located in the Scottish county of Peeblesshire.
Desertification, or loss of fertile, productive soil, is a problem which is exacerbating climate change, because the diminishing number of trees on the planet is worsening the greenhouse effect. One solution to this is reforestation. Despite its drawbacks, it is still an option for regreening thousands of hectares.
-
The plastics's invasion of the planet is a reality. Just remember that the plastic waste island floating in the Pacific Ocean now measures 1.6 million kmsup:2#. If we want to save the planet, the time has come for each and every one of us to take action.
Hydroponic crops are based on a practice that does away with soil and in its place uses a solution of water enriched with nutrients, among other alternatives. By using few resources, are seen as a option more sustainable solution than traditional agriculture. What's more, hydroponic crops can be grown at home!