Energy storage
The challenge of efficiently storing power
At Iberdrola, we are committed to energy storage as one of the great challenges to achieve the electrification and decarbonisation of the energy system.

At Iberdrola, we promote efficient energy storage as one of the key levers for electrification, decarbonisation and the energy transition. To this end, we use large-scale storage, through our pumped-storage hydropower plants, and small-scale storage, through lithium-ion batteries attached to renewable energy generation points. Our 2026 Strategic Plan foresees €1.5 billion of investment in this area. Our 2030 target: to reach more than 120 GWh of cumulative installed storage capacity.
Energy storage for the energy transition
At Iberdrola, we are convinced that investment in storage is one of the fundamental pillars for accelerating the electrification of our energy systems, along with clean generation infrastructures and smart grids.
But what is energy storage? Energy storage is the process of capturing and retaining energy for later release and use, which can be carried out using different technologies. This provision of energy enables the integration of intermittent electricity sources into the grid, such as solar and wind, expanding renewable energy’s supply and reducing dependence on fossil fuels. This in turn improves energy supply reliability and efficiency, as well as facilitating flexibility within the electricity market.
At Iberdrola, we are leaders in energy storage through hydroelectric and pumped-storage generation – the cleanest and most efficient storage method to date, with 4 GW of installed capacity. What's more, we are continuing to add various battery energy storage systems (BESS) to our portfolio of assets around the world. It’s a growing, versatile, efficient and customer-focused solution.
Promoting efficient energy storage
09 December 2025
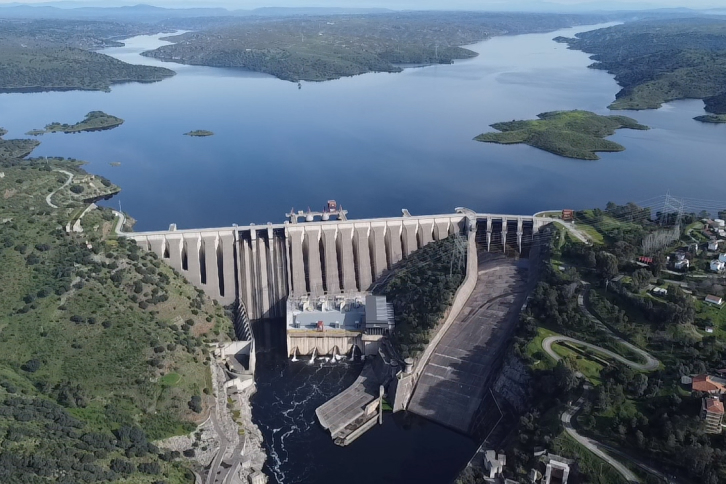
Pumped-storage hydropower system (PSHS)
Pumped-storage hydropower plants are like giant "natural batteries in a riverbed", storing energy at times of low demand by pumping water from a lower reservoir to an upper reservoir. When the need for electricity increases, that water is released downstream, activating the power-generating turbines. This system, which uses gravity and the water cycle, is renewable, efficient and clean.
Depending on the size of the upper and lower reservoirs, the height of the waterfall and the power of the turbines, these systems offer a wide range of power outputs: from several megawatt-hours (MWh) to several gigawatt-hours (GWh) of energy. They are an iconic example of how engineering can join nature in a respectful way to foster a more autonomous and sustainable energy future.
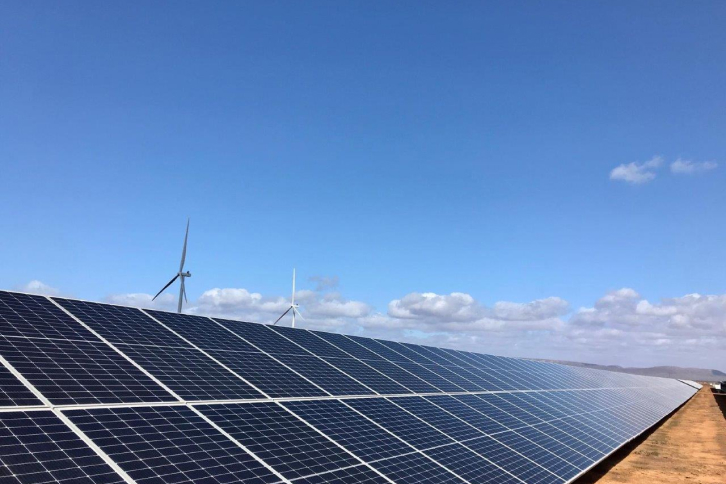
Battery energy storage system (BESS)
Battery energy storage systems (BESS) work by converting electricity into chemical energy by charging rechargeable batteries during times of low demand, and releasing it when we need it; for instance, during peak consumption.
There are several types of batteries for energy storage. Lithium-ion batteries are currently the most widely used due to their high energy density, long life cycle, and relatively low maintenance requirements.
Energy storage applications
Energy storage systems are divided into two categories: short-duration applications, which can adjust the power output in seconds of minutes to meet fluctuating demand, and long-duration applications, which provide stored power over hours or even days. The increasing integration of renewable sources into the electricity grid is driving the need for longer-duration storage solutions capable of ensuring a steady and reliable supply, even during extended periods of low renewable generation.
Using energy storage to manage renewable-energy fluctuations
- 2,000 GWh
- 1,500 GWh
- 1,000 GWh
- 500 GWh
- 0 GWh
- -500 GWh
- -1,000 GWh
- -1,500 GWh
- Hours

- 00
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- Net load
- Battery storage charge/discharge
Source: Iberdrola Capital Markets Day 2024 / Financial Times

"We need to invest in electricity distribution networks and storage – not only in short-term storage such as batteries, but long-term storage such as pumped-storage hydropower – as well as promoting interconnections between countries"
Ignacio S. Galán
Executive Chairman of Iberdrola
Iberdrola’s commitment to energy storage
Iberdrola's investment plans for the 2024-2026 period demonstrate a strong commitment to energy-storage technologies, recognising their crucial role in building a decarbonised energy system. We are allocating resources to both established solutions and emerging technologies, aiming to facilitate the integration of renewable energy and enhance the stability of power grids. These initiatives reflect the strategic importance of storage in the context of an accelerated global energy transition, through projects that strengthen the reliability and continuity of renewable energy supply across various grid scales.
Iberdrola’s commitment to electrification
- Investment in storage
€ 1.5 bn
- Investment in customers
€ 2.5 bn
- Renewable energy investment
€ 15.5 bn
- Energy network investment
€ 21.5 bn
- Total organic investment
€ 41 bn
- New hires 10,000
Source: Iberdrola Capital Markets Day 2024 / Financial Times
Our big energy storage projects
-
Tâmega: one of the largest hydroelectric projects in Europe in the last 25 years

-
We installed the UK's largest wind energy battery at Whitelee

-
Cortes - La Muela, Europe's largest hydroelectric power complex in Spain

-
Smithfield, our third commercial-scale battery in Australia

-
Aldeadávila, a unique hydroelectric engineering project in Spain

-
Gorman, our world's first commercial-scale battery system

Emerging solutions for energy-storage
Thermal energy is emerging as one of the key technologies for the future of energy storage. This mature technology is set to play a crucial role in decarbonising industrial heat, which currently accounts for 20% of global final energy demand and 10% of worldwide greenhouse gas emissions. The process involves storing heat in materials such as molten salts, ceramics, or concrete, which can then be directly used in industrial processes. Its advantages include large storage capacity, durations ranging from hours to days, and high efficiency, making it a promising solution for reducing the carbon footprint of energy-intensive sectors.
However, the development of energy storage technologies faces several challenges. These include the need for grid connectivity, limited awareness of these technologies among potential customers and regulators, and the lack of incentives in certain regions, including the European Union.
Other promising solutions include electrochemical- and mechanical-storage technologies. In the electrochemical domain, hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells store energy through chemical reactions. Mechanical storage includes systems like Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES), which compresses air and stores it in underground reservoirs, such as salt mines, to later release it and generate electricity when needed. These technologies complement existing solutions and expand the possibilities for a more sustainable and resilient energy grid.
The future of battery storage
Battery systems, particularly those based on lithium-ion (Li-ion) technology, have emerged as a competitive solution for energy storage. These batteries store energy through chemical reactions and are noted for their high efficiency, extremely fast response times to demand surges, and rapidly declining costs. However, they face significant challenges, including the risk of shortages and price volatility, largely driven by the growing dominance of the electric vehicle industry, which is significantly boosting demand for this technology.
Sodium-ion (Na-ion) batteries, made from abundant and cost-effective materials such as sodium, iron, and carbon, represent an exciting and viable alternative. These batteries deliver performance comparable to lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, with added advantages such as greater thermal stability and faster charging times. Major manufacturers such as CATL, BYD, HiNa and Natron have already announced plans to produce these batteries, both for grid storage applications and electric vehicles, underscoring their potential in advancing sustainable solutions.
More about energy storage
Energy storage: the key to a decarbonised future
Discover which storage systems are the most efficient and which one promises to drive the much-needed transition towards a decarbonised electrical system.
Efficient energy storageEnergy storage: the key to a decarbonised future
Discover which storage systems are the most efficient and which one promises to drive the much-needed transition towards a decarbonised electrical system.
Efficient energy storageArticles from our guest authors