Most innovative countries
Which are the world's most innovative countries?
What makes a country a benchmark for innovation (R&D)? Parameters such as the GII (Global Innovation Index) serve as a scale for discovering the most innovative countries. For this purpose, data provided by the WIPO (World Intellectual Property Organization) is used.

Switzerland is the world's leading producer of innovation for the 14th year in a row.

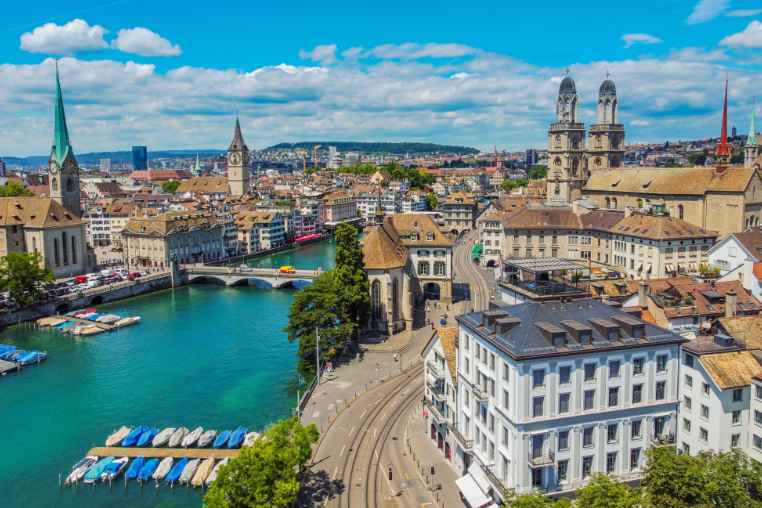
Sweden is bouncing back in infrastructure, business sophistication and researchers.

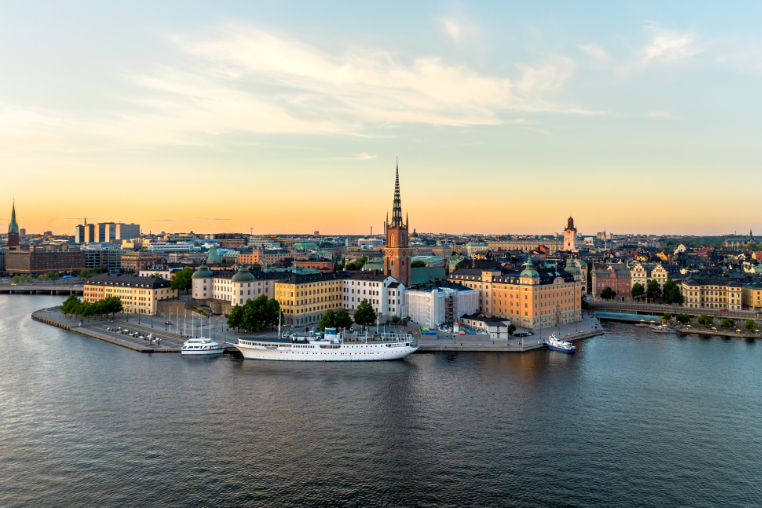
The United States once again stands out for the sophistication of its market and businesses.
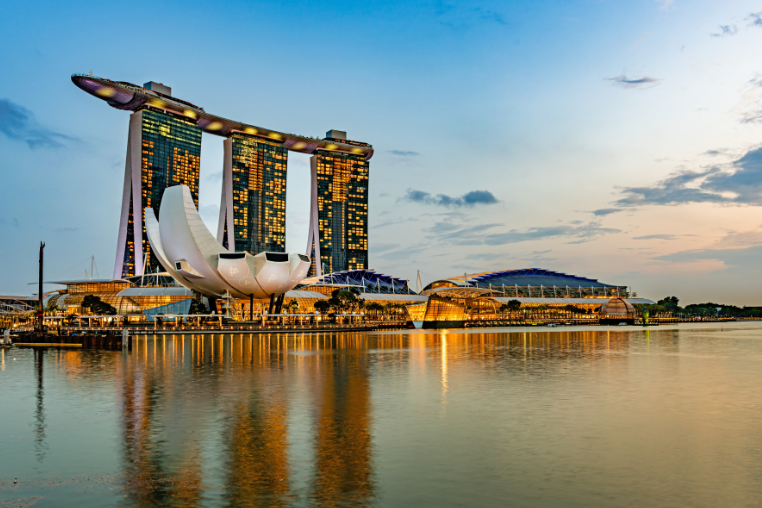

Singapore continues its growth in innovation and positions itself as a leading Asian country.
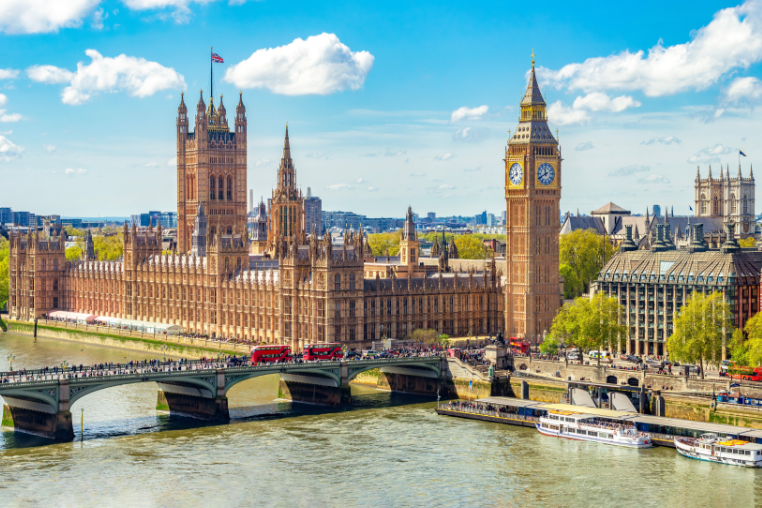

The UK drops to fifth position but maintains a high level of market sophistication.
For the 14th consecutive year, Switzerland is the most innovative economy in 2024, according to the Global Innovation Index (GII) External link, opens in new window. . Based on data from the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), it analyses the economic data of 133 countries and ranks their position in various categories such as research, infrastructure or creativity in their proposals. This allows countries to be ranked and to explore which countries have improved in recent years.
External link, opens in new window. . Based on data from the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), it analyses the economic data of 133 countries and ranks their position in various categories such as research, infrastructure or creativity in their proposals. This allows countries to be ranked and to explore which countries have improved in recent years.
What is the Global Innovation Index?
The GII report focuses on assessing innovation at all levels in 133 countries around the world. To do so, it investigates a country's own research spending, its efforts in education, the number of science-related publications and many other parameters, always divided according to the country's economic level.
For this report it is vital to know which countries are performing above the expectations placed on them and which are at the expected level. That is why the GII divides countries into four levels:
- High economic level: Includes practically all the countries of the European Union, Asian countries such as Japan and South Korea, in Oceania Australia and New Zealand as well as several Middle Eastern and American countries.
- Upper-middle economic level: This includes most of the emerging countries and also other American countries, as well as the first African countries. Their economies are moving towards the top positions and their growth is remarkable.
- Lower-middle economic level: Includes countries such as India and Vietnam, as well as most of the African continent and Asia.
- Low economic level: Includes African countries and Yemen, as they have the lowest GDP per capita and are therefore the most difficult countries to invest in.
In the division we discussed previously, three measures can be seen, those countries that are innovating above their group (the clearest example is China, 11th in the overall ranking despite belonging to the second group), those that are doing at the average of the group and those that are below expectations.
The world's most innovative countries
The GII determines that the 10 most innovative countries in the world are:

Digital transformation
Boosting business strategy through digitisation.

PERSEO programme
Over 15 years committed to start-ups and innovation.

Our innovation hubs
Find out how we promote training and research in our centres.

Fourth Technological Revolution
Industry 4.0 is a fusion of leading-edge production techniques and smart systems.