History of solar energy
Development and progress in photovoltaic solar energy
Photovoltaic energy Renewable energy
The first solar panel in history came into being at the end of the 19th century, but the use of the sun as an energy source dates back to the very origins of mankind. The history of photovoltaic technology has been shaped by various scientific advances that came one after another to obtain electricity from the sun. Find out about its origin, its evolution and why it’s one of the main sources of renewable energy.


The advent of solar panels in different sectors of society has transformed the way energy is generated and consumed.
Humans have always been curious about and admired the sun, the dominant star in our sky and the protagonist of various legends. It’s not surprising that different cultures all around our planet and over the course of time have found in the sun a divinity to be worshipped - for the Greeks under the name of Helios, for the Egyptians as Ra or for the Incas as Inti. But, above all, it is the energy that provides us with light and heat and one of the main sources of life for living beings, as it allows them to develop.
Successive scientific advances have made it possible to understand the star and explore its uses on Earth. Today, it’s an essential resource in the midst of the energy transition thanks to the strong push to photovoltaic solar energy. Let’s take a look at the history of this technology, the main figures in its evolution and its benefits.
Origin of Photovoltaic Solar Energy
The practical use of the sun's energy in early civilisations was very limited due to the scarcity of efficient technology and responded to a basic understanding of how to integrate it into everyday needs. Initially, the sun's rays were amplified to create fire. Later, the Greeks and Romans in the ancient world used solar energy indirectly to heat the house and water for bathing and even developed architecture that made the most of sunlight and heat during the day and maintained it at night.
First Applications of Photovoltaic Solar Energy
Beyond these primitive uses of solar energy, the first major milestone in photovoltaic history came in 1839, when the French physicist Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel discovered the photoelectric effect. While experimenting with an electrolytic cell, the researcher noticed that current flowed up one of the electrodes when exposed to sunlight. The discovery paved the way for inventors all over the world to devise new devices using this technique.
One of the first applications was the creation of the first parabolic solar collector in 1866. French researcher Augustin Mouchot created a machine in the middle of the 19th century capable of extracting solar energy for commercial purposes. The sun's rays were concentrated by a series of mirrors on a boiler with water and the steam generated by the boiling water drove a steam engine.
First Solar Cell
It was during this period that the electrical engineer Willoughby Smith, who used selenium rods to detect faults in submarine cabling, discovered a strange phenomenon: the conductivity of the rods increased exponentially when exposed to solar energy. Smith published his findings in 1873 in the Journal of the Society of Telegraph Engineers.
Following Smith's publication and after conducting numerous experiments, two British scientists, William Grylls Adams and Richard Evans Day, concluded that "current could only be produced in selenium by the action of light". Adams and Day then discovered that light produced a flow of electricity through a solid material and named this current "photoelectric".
Continuing research in the area led in 1883 to the American inventor Charles Fritts building the first solar cell, which had an efficiency of about 1%. The prototype, which generated a direct current under both direct and diffuse light exposure, consisted of a metal panel with a layer of selenium and a layer of gold.

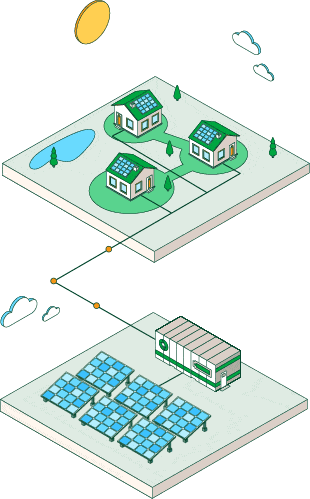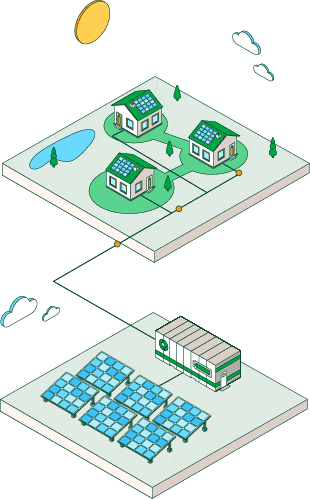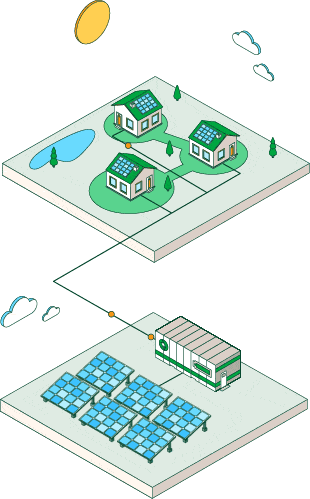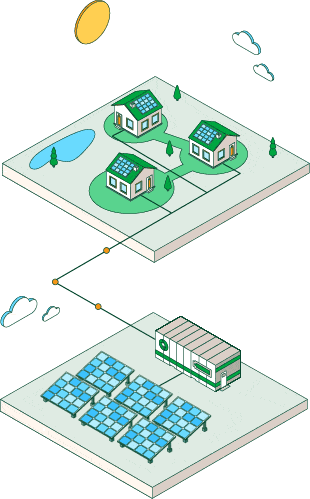
Photovoltaic plants
Photovoltaic solar energy is obtained by converting sunlight into electricity.

Photovoltaic solar panels: what they are
Photovoltaic solar panels are key to the implementation of solar energy.

Photovoltaic energy terms
Top 10 terms to know about photovoltaic energy.

Recycling of solar panels
How does solar panel recycling work?
The Modern Era and Solar Panels
When solar photovoltaics became commercially available in the 1950s, the price of solar panels was very high for the general public and their practical application was mainly in the aerospace industry. They were used to power external equipment like satellites by the United States and the Soviet Union.
Despite this initial momentum in space, the use of solar energy in domestic and commercial applications was low in the following decades. This was due to how cheap fossil fuels were, which dominated the energy market and still offered a more affordable alternative to solar energy.
However, the situation changed in the 1970s and 1980s with the oil crisis. The rising price of fossil fuels caused the public and the scientific community to look with interest to renewable energy. Technology development was boosted, technical efficiencies were improved - with solar tracking and energy storage technologies - and production costs were cut, making solar energy an affordable alternative.
The advent of solar panels at home and in different areas of society
Thanks to incentive policies, the sun has become a promising solution for air conditioning, water heating and electricity generation in households and industry. It is the seed of photovoltaic self-consumption, which is becoming increasingly common in different areas of society:
Advantages of photovoltaic solar energy
Optimal for rural areas
A system suitable where power lines do not reach or are difficult to install
Modulable according to need
It can be produced in small generator installations and in large photovoltaic plants
Green jobs
Contributes to the creation of green jobs and local economic growth
More information SEE INFOGRAPHIC: Advantages of photovolaic solar energy [PDF]
SEE INFOGRAPHIC: Advantages of photovolaic solar energy [PDF]
Evolution of Solar Panels
Despite the production of the early photovoltaic cell in the 19th century, it was not until the middle of the next century that a practical model became available. In 1954, Bell Laboratories developed the first silicon solar cell, a material with an efficiency of 6%. This breakthrough showed that converting sunlight into electricity could be done and a market opportunity at that.
This event marked the beginning of a continuous evolution of solar panels. During the 1960s and 1970s, silicon purity and manufacturing techniques were improved, which allowed the efficiency of solar cells to be raised to around 14%. The following decades were marked by the introduction of thin-film solar cells and material improvements with new alternatives such as cadmium telluride, heterojunction and perovskite.
As early as the 2000s, monocrystalline silicon began to be used, which made it possible to achieve an efficiency of 20%, followed by polycrystalline silicon, which helped to save on manufacturing costs. Moreover, the combination of this material with perovskite made it possible to achieve efficiencies of more than 25% in the laboratory.
In recent years, the manufacture of bifacial solar panels, which provide additional radiation gain on both the front and rear faces, and floating photovoltaics, which use the surface of large bodies of water to install panels, have gained in prominence. Future trends point to the manufacture of organic and quantum dot solar cells, which promise greater flexibility and lower costs, as well as the use of transparent solar panels, which allow them to be integrated into windows and other architectural elements without compromising their aesthetics.